CONTACTLESS
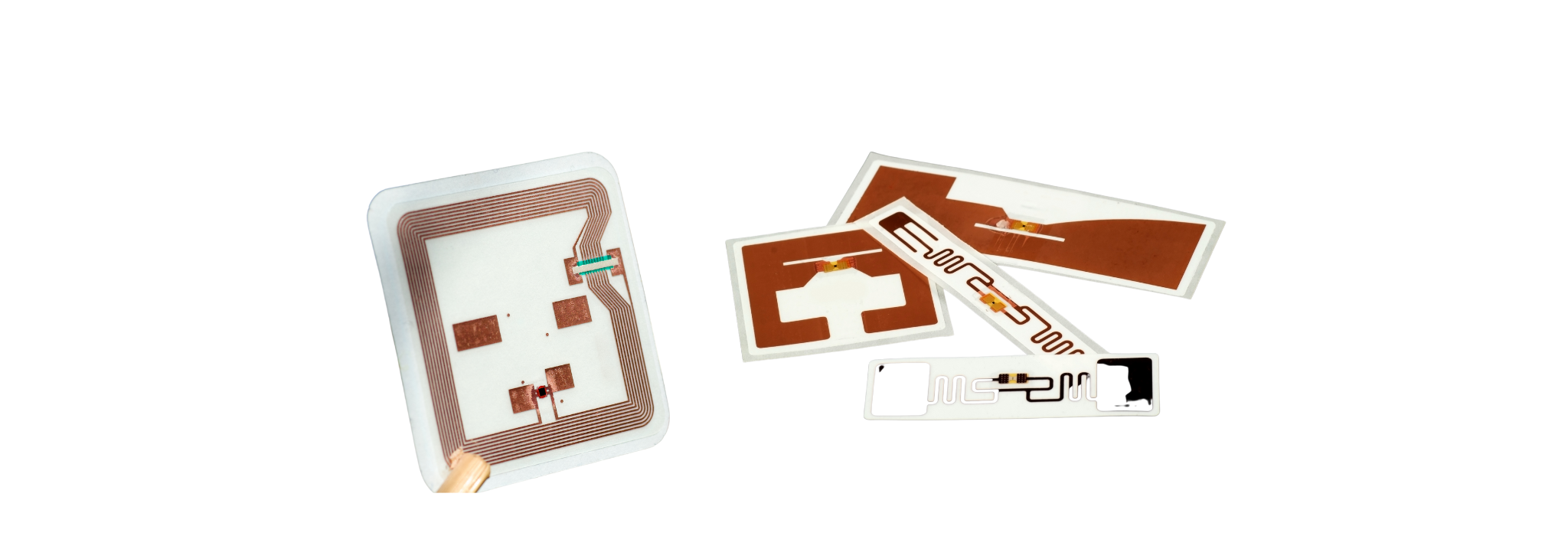
RFID uses tags or transponders to store and remotely retrieve data. Contactless cards with embedded silicon processors and antennas can respond to RFID queries. Contactless cards aren't powered. The incoming radio frequency signal induces a tiny electrical current in the antenna, which powers the card's CMOS IC and enables it to transmit a response. Passive tags reflect the reader's carrier signal. This means the aerial (antenna) can both receive and emit backscatter signals. Passive RFID tags can store data in nonvolatile EEPROM in addition to a GUID. Depending on radio frequency and antenna design/size, passive tags can be read from a few millimetres to a few metres (EPC and ISO 18000-6). Passive RFID tags have an endless lifespan, no batteries, and are smaller.
Contactless 1 KB:
Functional Specifications:
Mifare RF Interface (ISO/IEC14443 A)
- Contactless transmission of data and supply energy (no battery needed)
- Operating distance: Up to 100 mm (depending on antenna geometry)
- Operating Frequency: 13.56 MHz
- Fast data transfer: 106 Kbit/s
- High Data Integrity: 16 bit CRC, parity, bit coding, bit counting
- True Anti-collision
- Typical Ticketing transaction: < 100 ms (including back-up management)
EEPROM:
- 1 Kbyte –organized in 16 sectors with 4 blocks of 16 bytes each (One block consists of 16 bytes)
- User definable access conditions for each memory block
- Data Retention: 10 years
- Write Endurance: 100,000 cycles
Security:
- Mutual three-pass authentication
- Data encryption on RF-channel with reply attack protection
- Individual set of two keys per sector (per application) to support multi-application with key hierarchy
- Unique serial number for each device
- Transport key protects access to EEPROM on chip delivery
Card Dimensions:
- 2.125'' x 3.375'' x 0.033'' max. (5.40 x 8.57 x 0.084 cm)
- Thin, Flexible Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)Laminate
- -13 to 158 F (-25 to 70 degree Celsius)
- Contactless transmission of data and powered by RF-field (no battery)
- Operating Distance: Up to 100 mm (depending on antenna geometry)
- Operating Frequency: 13.56 MHz
- Fast data transfer: 106Kbit/s, 212 Kbit/s, 424 Kbit/s
- High data integrity: 4 Byte MAC, 16 Bit CRC, parity, bit coding, bit counting
- True deterministic anti-collision
- 7 byte unique identifier (cascade level two according to ISO 14443-3)
- Uses ISO 14443-4 transport protocol
- 4 Kbyte NV-Memory
- NV-Memory write time 2 ms (1 ms erase, 1 ms program)
- Data retention of 10 years
- Write endurance 100,000 cycle
- Flexible File system
- Up to 28 applications simultaneously on one PICC
- Up to 16 files in each application
- Unique 7 Byte serial number for each device
- Mutual three pass authentication
- Hardware DES/3DES Data encryption on RF-channel with replay attack protection
- Data Authenticity by 4 Byte MAC
- Authentication on Application level
- 2.125'' x 3.375'' x 0.033'' max. (5.40 x 8.57 x 0.084 cm)
- Thin, Flexible Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)Laminate
- 13 to 158 F (-25 to 70 degree Celsius)
Card Construction:
Operating Temperature:
CONTACTLESS 4 KB WITH DES & TDES SECURITY:
Functional Specifications:
RF Interface: ISO 14443 Type A
Non-Volatile Memory:
NV-Memory Organisation:
Security:
Card Dimensions:
Card Construction:
Operating Temperature:
Contactless 4 KB:
Functional Specifications:
Mifare RF Interface (ISO/IEC14443 A)
- Contactless transmission of data and supply energy (no battery needed)
- Operating distance: Up to 100 mm (depending on antenna geometry)
- Operating Frequency: 13.56 MHz
- Fast data transfer: 106 Kbit/s
- High Data Integrity: 16 bit CRC, parity, bit coding, bit counting
- True Anti-collision
- Typical Ticketing transaction: < 100 ms (including back-up management)
EEPROM:
- 4 Kbytes –organized in 32 sectors with 4 blocks and 8 sectors with 16 blocks (One block consists of 16 bytes)
- User definable access conditions for each memory block
- Data Retention: 10 years
- Write Endurance: 100,000 cycles
Security:
- Mutual three-pass authentication
- Data encryption on RF-channel with reply attack protection
- Individual set of two keys per sector (per application) to support multi-application with key hierarchy
- Unique serial number for each device
- Transport key protects access to EEPROM on chip delivery
Card Dimensions:
- 2.125'' x 3.375'' x 0.033'' max. (5.40 x 8.57 x 0.084 cm)
- Thin, Flexible Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)Laminate
- 13 to 158 F (-25 to 70 degree Celsius)
- Contactless transmission of data and supply energy (no battery needed)
- Operating Distance: Up to 100 mm (depending on antenna geometry)
- Operating Frequency: 13.56 MHz
- Fast data transfer: 106Kbit/s
- High data integrity: 16 Bit CRC, parity, bit coding, bit counting
- True anti-collision
- 7 byte serial number (cascade level two according to ISO 14443-3)
- Typical ticketing transaction: < 35 ms
- Fast counter transaction: < 10 ms
- 512 bit, organised in 16 pages with 4 byte each
- Field programmable read-only locking function per page
- 32 bit user definable One Time Programmable (OTP) area
- 385 bit user r/w area (12 pages)
- Data retention of 5 years
- Write endurance 10,000 cycles
- Anti-cloning support by unique 7 Byte serial number for each device
- 32 Bit user programmable OTP area
- Field programmable read-only locking function per page
- 2.125'' x 3.375'' x 0.033'' max. (5.40 x 8.57 x 0.084 cm)
- Thin, Flexible Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)Laminate
- -13 to 158 F (-25 to 70 degree Celsius)
Card Construction:
Operating Temperature:
CONTACTLESSS 64 BYTES:
Functional Specifications:
Mifare RF Interface (ISO / IEC 14443A)
Non-Volatile Memory:
Security:
Card Dimensions:
Card Construction:
Operating Temperature:
DUAL
Both contactless RFID readers and traditional terminals can read Kyrotec's dual-sided cards. The fact that these cards can serve multiple purposes (attendance, electronic wallet, loyalty programme membership, etc.) is undoubtedly one of their greatest benefits.
